 Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate is known as parthenogenesis.
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without a mate is known as parthenogenesis. cloning, the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination.
cloning, the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Cloning happens often in nature—for example, when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination.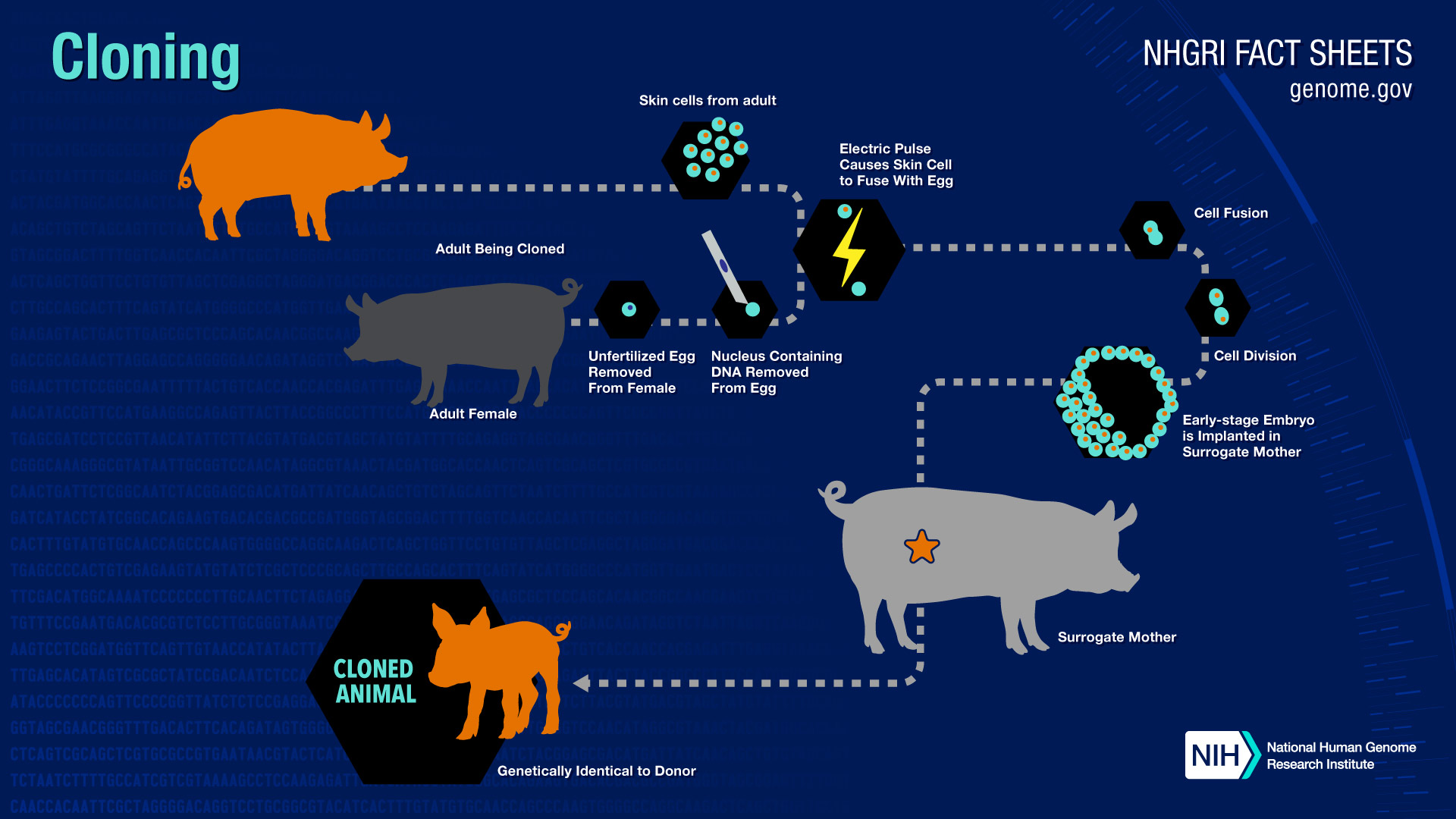 The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials, including genes, cells, tissues and even entire organisms, such as a sheep.
The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone. Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials, including genes, cells, tissues and even entire organisms, such as a sheep. 1. To make multiple identical copies of (a DNA sequence). 2. To create or propagate (an organism) from a clone cell: clone a sheep. 3. To reproduce or propagate asexually: clone a plant variety. 4. To produce a copy of; imitate closely: "The look has been cloned into cliché" (Cathleen McGuigan).
1. To make multiple identical copies of (a DNA sequence). 2. To create or propagate (an organism) from a clone cell: clone a sheep. 3. To reproduce or propagate asexually: clone a plant variety. 4. To produce a copy of; imitate closely: "The look has been cloned into cliché" (Cathleen McGuigan).